ParaView:Build And Install: Difference between revisions
| Line 403: | Line 403: | ||
* Don't use <font color="red">make install</font> as it may install more files than required. | * Don't use <font color="red">make install</font> as it may install more files than required. | ||
* CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX is not applicable when using cpack and will have no effect. | * CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX is not applicable when using cpack and will have no effect. | ||
* Build trees of ParaView on non-Windows systems, always have RPATH information embedded in the binaries. When a make install is performed or CPACK is used, all RPATH information is stripped from the binaries. By default ParaView builds forwarding executables (launchers) that are installed in the | * Build trees of ParaView on non-Windows systems, always have RPATH information embedded in the binaries. When a make install is performed or CPACK is used, all RPATH information is stripped from the binaries in the install tree. By default ParaView builds forwarding executables (launchers) that are installed in the bin directory. These binaries properly setup the environment to launch the equivalent executable in the lib/paraview-x.y directory. | ||
== Notes == | == Notes == | ||
Revision as of 12:57, 21 July 2010
Introduction
This page describes how to build and install ParaView. It covers both the release and the development versions. Also, it covers both Unix-type systems (Linux, HP-UX, Solaris, Mac) as well as Windows.
Prerequisites
The ParaView build process requires CMake version 2.6.4 or higher and a working compiler. On Unix-like operating systems, it also requires Make, while on Windows it requires Visual Studio (8 or later).
Building ParaView's user interface requires Trolltech's Qt, version 4.3.* (4.3.5 recommended) Qt is dual licensed. To compile ParaView, either the open or commercial version may be used. If you intend to make changes the ParaView's GUI and distribute the results, you must obtain a commercial license. The open source version of Qt can be found here [1]. Commercial licenses can be purchased directly from TrollTech [2]. For more information on what can be done with the open source version, read this [3].
In order to run ParaView in parallel, MPI [4], [5] is also required.
In order to use scripting, python is required [6].
Download And Install CMake
CMake is a tool that makes cross-platform building simple. On several systems it will probably be already installed. If it is not, please use the following instructions to install it. If CMake does not exist on the system, and there are no pre-compiled binaries, use the instructions below on how to build it.
Use Binaries
There are several precompiled binaries available at the CMake download page.
On Unix-like operating systemsLet's say on Linux, download the appropriate version and follow these instructions: cd $HOME wget http://www.cmake.org/files/v2.4/cmake-2.4.5-Linux-i386.tar.gz mkdir software cd software tar xvfz ../cmake-2.4.5-Linux-i386.tar.gz
|
On Windows
On Windows, if you are not administrator
|
Build Your Own CMake
On Unix-like operating systemsDownload the source code http://www.cmake.org/files/v2.4/cmake-2.4.5.tar.gz cd $HOME wget http://www.cmake.org/files/v2.4/cmake-2.4.5.tar.gz tar xvfz cmake-2.4.5.tar.gz mkdir cmake-2.4.5-bin cd cmake-2.4.5-bin ../cmake-2.4.5/bootstrap --prefix=$HOME/software make make install
|
On WindowsTo build CMake on windows, a previous version of CMake is required. This can be downloaded from the CMake download page. |
Build ParaView
Download ParaView Source Code
If you are trying to build a ParaView release, download it from the release page. For the development version, please follow the instructions below for checking it out from CVS.
Download The Release
You can always download the binaries from ParaView download page. This page contains binaries for several platforms and the source code for the releases.
Note: debian build
List of packages to build ParaView on Debian:
libphonon-dev libphonon4 libqt4-assistant qt4-dev-tools libqt4-core libqt4-gui qt4-qmake libxt-dev g++ gcc cmake-curses-gui libqt4-opengl-dev mesa-common-dev
With MPI (using openmpi, you can use any other flavour):
openmpi-common openmpi-bin libopenmpi-dev
With Python:
python2.5-dev
Checkout Development Version from CVS
On Unix-like operating systemsmkdir $HOME/projects cd $HOME/projects cvs -d:pserver:anoncvs@www.paraview.org:/cvsroot/ParaView3 login <enter> cvs -d:pserver:anoncvs@www.paraview.org:/cvsroot/ParaView3 co ParaView3 |
On WindowsIf you have Cygwin or Mingw shell, then use them, and follow the instructions for Unix-like oprating systems.
If you are on Windows and do not have Cygwin or Mingw shell, please download a CVS client. We recommend TortoiseCVS, which is a GUI for CVS on Windows.
The following parameters are used for TortoiseCVS:
|
Configure ParaView With CMake
- Always use a separate build directory. Do not build in the source directory.
On Unix-like systems
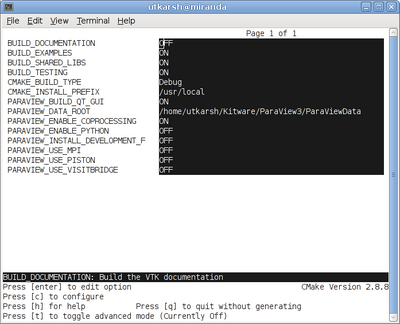
mkdir $HOME/projects/ParaView-bin cd $HOME/projects/ParaView-bin ccmake $HOME/projects/ParaView3 About CCMake (Curses CMake GUI)
|
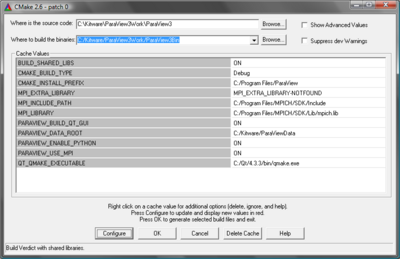
On Windows
About CMakeSetup (Windows CMake GUI)
|
ParaView Settings
| Variable | Description |
| BUILD_SHARED_LIBS | If ON, use shared libraries. This way executables are smaller, but you have to make sure the shared libraries are on every system on the cluster. |
| PARAVIEW_USE_MPI | Turn this to ON to enable MPI. Other MPI options will not be available until you turn this on. |
| MPI_LIBRARY | Path to the MPI library (such as /usr/lib/libmpi.so). Should be found by default, but you may have to set it. (see the note below) |
| MPI_EXTRA_LIBRARY | Path to extra MPI library (such as /usr/lib/libmpi++.so). If the MPI distribution is MPICH, this may not be found; in this case, it is ok for this variable to be set to MPI_EXTRA_LIBRARY-NOTFOUND. |
| MPI_INCLUDE_PATH | Path to MPI includes (such as /usr/include/mpi). Again, this should be found by default. |
| PARAVIEW_ENABLE_PYTHON | Makes python client scripting and the python programmable filter available. |
| PARAVIEW_BUILD_QT_GUI | Flag to enable/disable the building of the ParaView Qt-based client. This option is useful when building paraview on server nodes or when we are only interested in the python client, as it avoids building of the Qt client thus does not require Qt. ON by Default. |
| QT_QMAKE_EXECUTABLE | Path to Qt's qmake executable (such as /usr/local/Trolltech/Qt-4.2.2/bin/qmake). Cmake uses this to locate the rest of the required Qt executables, headers and libraries. |
| VTK_USE_CARBON | For Mac, this is the default. Neither X11 nor COCOA frameworks are supported. |
Note for MPI settings: If your MPI variables aren't set automatically (usually the case if the compiler wrapper [mpicxx] is not in the path or in some standard directory), toggle advanced options and set MPI_COMPILER variable to the full path of your mpi compiler (usually mpicxx), and configure. This should set all the required MPI variables. If not, then you might need to enter them manually.
Finish Configuring ParaView
Using CCMake
|
Using CMakeSetup
|
Build ParaView
You can now build ParaView using the appropriate build system.
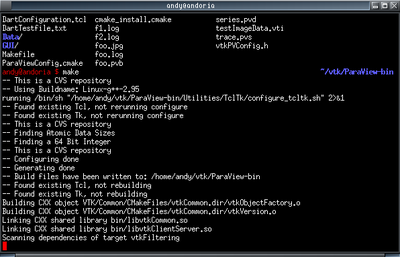
Using MakeCMake will now generate Make files. These makefiles have all dependencies and all rules to build ParaView on this system. You should not however try to move the build directory to another location on this system or to another system. Once you have makefiles you should be able to just type: make
make -j 4
make HTMLDocumentation |
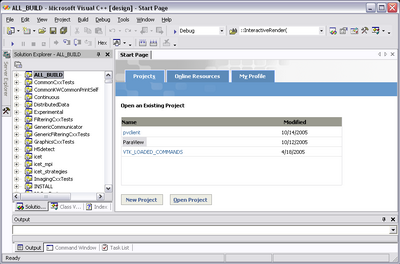
Using Visual StudioCMake will now create Visual Studio project files. Before you open Visual Studio, be sure that the Qt .dlls are in your path. You should now be able to open the ParaView project (or workspace) file. Make sure to select the appropriate build type (Debug, Release, ...). To build ParaView, simply build the ALL_BUILD target. The ParaView build does not create the online documentation by default. Select the HTMLDocumentation target, right click, and select Build. |
Install ParaView
ParaView can be run directly from the build directory. That said, for production environments, it should be installed in some system location. For that purpose simply follow the instructions for "Distributing ParaView" and the unpack the generated archive at the appropriate install location.
Distributing ParaView
It is possible to create distribution binaries for ParaView using CPack which is included in CMake. The packaged binary can be in any of the variable supported generator formats eg. DEB (debian packages), RPM (RPM Packages), NSIS (Null Soft Installer) etc. Please refer to [[7]] for a complete list.
CMake Variables
When building ParaView so that it can be distributed, in most typical cases, ensure that the values for the following CMake variables are set correctly.
| Variable | Value | Description |
| BUILD_SHARED_LIBS | ON | Enables shared libraries (unless you are sure you want to do static builds) |
| CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE | Release | Unless you want to end up with debug install, set this to Release |
| PARAVIEW_USE_MPI | OFF | Unless you are taking extra steps to ensure that the clients have the required MPI libraries, set this to OFF, since ParaView does not include rules to package MPI. |
| PARAVIEW_ENABLE_PYTHON | OFF | Unless you are taking extra steps to ensure that clients have the rquired python libraries/modules. |
| PARAVIEW_GENERATE_PROXY_DOCUMENTATION | ON | To ensure that the html documentation for the sources/filters/readers/writes is generated and packed into the application, turn the following flag ON. |
| PARAVIEW_INSTALL_DEVELOPMENT | OFF/ON | To package development files so that people can build plugins/custom-apps using the installation. |
| PARAVIEW_BUILD_QT_GUI | ON/OFF | To enable building the Qt client |
PARAVIEW_EXTRA_INSTALL_RULES_FILE: Adding custom install rules
You can add additional install rules by writing a custom cmake file with install rules and then set PARAVIEW_EXTRA_INSTALL_RULES_FILE cmake variable to point to that file. ParaView process all install rules that have the COMPONENT set to either "Runtime" (for executables), or "RuntimeLibraries" (for shared libraries), or "BrandedRuntime" (for custom-application specific libraries/executables) only (and "Development" when PARAVIEW_INSTALL_DEVELOPMENT is TRUE). So you want to add your install rules with appropriate COMPONENT values in this custom cmake file.
e.g. you want to include mpilibs in the installation, in that case the custom install rules file could look something as follows:
<source lang="python">
INSTALL (FILES ${MPI_LIBRARY} ${MPI_EXTRA_LIBRARY}
DESTINATION ${PV_INSTALL_LIB_DIR}
COMPONENT RuntimeLibraries)
</source>
Generate Package
Following the configuration, simply run 'make' to compile and build.
|
On Unix-like operating systems To generate a tar ball, in the binary directory, simply run cpack -G TGZ --config {ParaViewBuildDir}/Applications/ParaView/CPackParaViewConfig.cmake
If PARAVIEW_BUILD_QT_GUI was OFF, then to generate a package consisting of the server executables alone, use the following command: cpack -G TGZ --config {ParaViewBuildDir}/Servers/Executables/CPackParaViewServersConfig.cmake
|
On Windows, to generate a null-soft installer (requires [8]), in the binary directory, simply run cpack -G NSIS -C Release --config {ParaViewBuildDir}/Applications/ParaView/CPackParaViewConfig.cmake
If PARAVIEW_BUILD_QT_GUI was OFF, then to generate a package consisting of the server executables alone, use the following command: cpack -G NSIS -C Release --config {ParaViewBuildDir}/Servers/Executables/CPackParaViewServersConfig.cmake
|
|
On Mac, to generate an app bundle that can be distributed, use cpack -G DragNDrop --config {ParaViewBuildDir}/Applications/ParaView/CPackParaViewConfig.cmake
If PARAVIEW_BUILD_QT_GUI was OFF, then to generate a tarball consisting of the server executables alone, use the following command: cpack -G TGZ -C Release --config {ParaViewBuildDir}/Servers/Executables/CPackParaViewServersConfig.cmake
|
Miscellaneous Comments
- Don't untar the packaged tar ball over the build directory itself. You can always remove the build directory and untar the tar ball in its place.
- Don't use make install as it may install more files than required.
- CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX is not applicable when using cpack and will have no effect.
- Build trees of ParaView on non-Windows systems, always have RPATH information embedded in the binaries. When a make install is performed or CPACK is used, all RPATH information is stripped from the binaries in the install tree. By default ParaView builds forwarding executables (launchers) that are installed in the bin directory. These binaries properly setup the environment to launch the equivalent executable in the lib/paraview-x.y directory.
Notes
Compiling on the Mac
To compile on the Mac, follow the instructions for Unix. The recommended configuration settings are: BUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON.
Environment Variables
If you build with shared libraries, you may have to add the Qt directory to you PATH environment variables to run paraview. On windows one way to do so is to open up the environment variables dialog by clicking through Start->Control Panel->System->Advanced->Environment Variables. From that dialog add a new user variable called PATH with a value of C:\Qt\4.2.2\bin. For other operating systems, add Qt/4.2.2/lib to your LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable.