IMServer:Uploader: Difference between revisions
From KitwarePublic
Jump to navigationJump to search
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
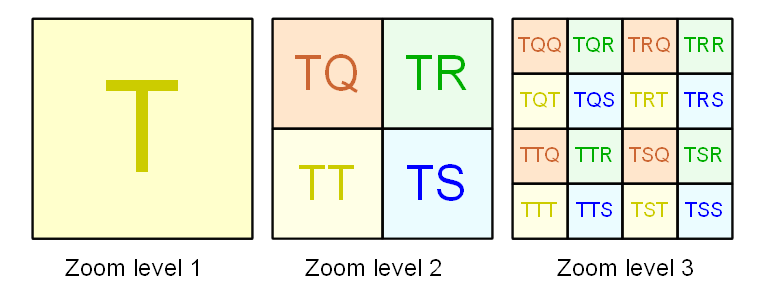
[[File:IMServerMultiresNamingConvention.png | Naming of images for multiresolution representation]] | [[File:IMServerMultiresNamingConvention.png | Naming of images for multiresolution representation]] | ||
== Uploading images into database == | |||
* Either dice the large images first and store in .mrj (Multi-res JPEG) format and later read from the MultiResolutionJPEGSource and insert the binary tile chunk into database one by one. | |||
* Or Start the dicing process, and without any disk access, keep inserting into the MongoDB as and when every tile chunk is generated. | |||
== Upload to MongoDB == | == Upload to MongoDB == | ||
Revision as of 20:38, 24 January 2011
Image Dicer
Large images are split into multir-esolution representation
The files are padded to cover next power of two, and then
Uploading images into database
- Either dice the large images first and store in .mrj (Multi-res JPEG) format and later read from the MultiResolutionJPEGSource and insert the binary tile chunk into database one by one.
- Or Start the dicing process, and without any disk access, keep inserting into the MongoDB as and when every tile chunk is generated.
Upload to MongoDB
A simple mongo interface is created
<source enclose=pre lang="c">
- include <iostream>
- include <client/dbclient.h>
using namespace std;
class vtkMongoInterface {
mongo::DBClientConnection conn;
public:
// Constructor
vtkMongoInterface() {}
// Operations possible int connect(const char *server = "127.0.0.1", int port = 27017); int insert(const char * name , int num ); int insert(const char * path, mongo::BSONObj obj); int query();
};
</source>