CMake:Eclipse UNIX Tutorial
Obtaining Eclipse + CDT
Eclipse IDE is an IDE written in Java that was initially used for developing java programs. Eclipse is also a "Rich Client Platform" on which almost any type of application can be built. One such project is the "C/C++ Development Tools" or CDT. The home page is here.
You can download a version of Eclipse that does NOT include all the other Java Development tools and only includes the C/C++ tools here. Just select the "Eclipse IDE for C/C++ Developers" link on that page.
There is also an Eclipse/CDT distribution for Windows that specifically includes MinGW/MSys/JRE/CDT. The home page is here.
CMake Editor Plugin for Eclipse
There is also an editor plug-in for Eclipse available (see above): CMake Editor.
Eclipse + CDT Version Information
CDT 3.1.2 goes with Eclipse 3.2
CDT 4.0 goes with Eclipse 3.3.
I highly recommend CDT 4.0 as the feature set is vastly improved, most notably the indexer which has become super fast. The syntax highlighting improvements are also very nice. There are now at least 3 C/C++ code formatters available (or edit/create your own style rules). Numerous other improvements are also incorporated into the release. Eclipse 3.3 does require Java 1.5 (5.0) jvm.
File System Setup
Eclipse CDT supports projects that already provide a makefile so this is good news for CMake users.
The basic steps to get Eclipse + CDT + CMake working are:
- Use CMake to generate makefiles for your project
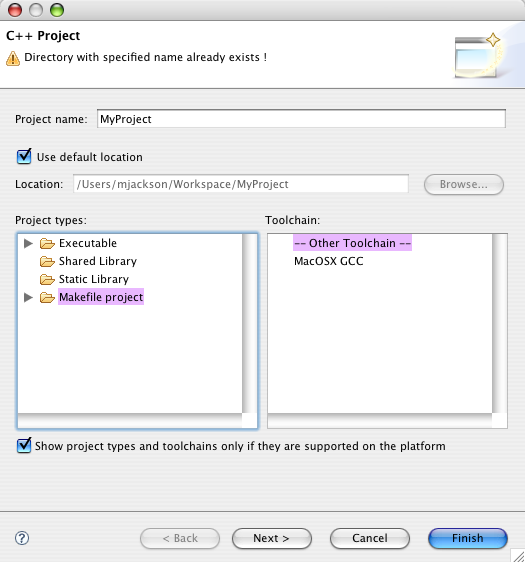
- Create a new project in Eclipse using the top level directory of your project as the "Project Directory".
- Create an "External Tool" to run cmake from within Eclipse (Optional)
Eclipse CDT works better if the build files are somewhere in project directory such as a subdirectory (for example 'Build').
A typical project setup workflow would be something like this.
In a terminal program "cd" into the top level of your project directory ideally where your CMakeLists.txt file resides. Create a directory called "Build". cd into Build and then run 'ccmake' or 'cmake' using the parent directory as the target for cmake. So, for example if we have a project called "MyProject" located in /Users/mike/Projects, then the terminal commands would look like the following:
[mjackson@Thor:]$ cd /Users/mike/Workspace/MyProject [mjackson@Thor:]$ mkdir Build [mjackson@Thor:]$ cd Build [mjackson@Thor:]$ ccmake ../
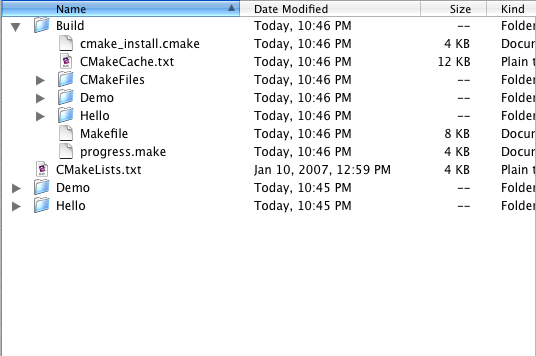
Image showing the basic Project setup for our tutorial.
At this point we have bootstrapped the process somewhat so Eclipse throws less errors when we setup the Eclipse Projects.
Eclipse Project Setup
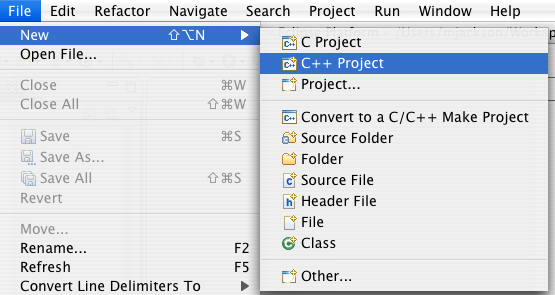
Launch Eclipse and go to "New->C++ Project" Menu
Select the MakeFile Project type
Select the Advanced Settings Button
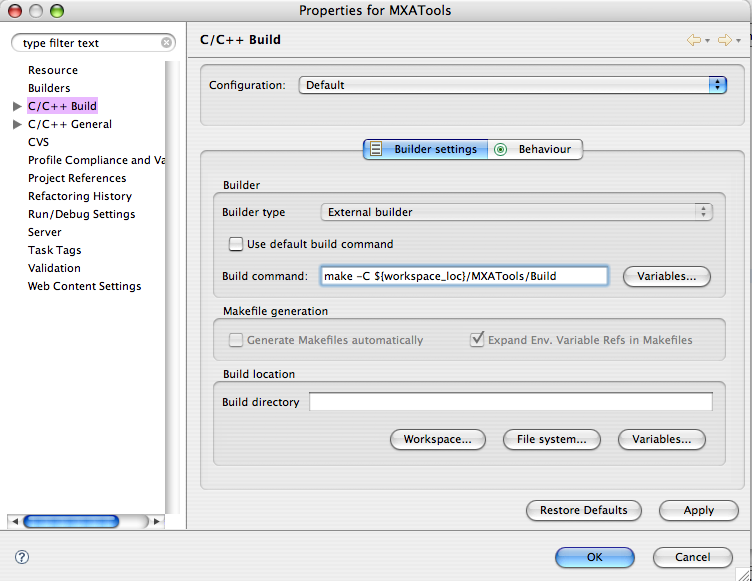
Uncheck the Use Default Build Command
Insert the following in the Build Command Text Field: make -C ${project_loc}/Build
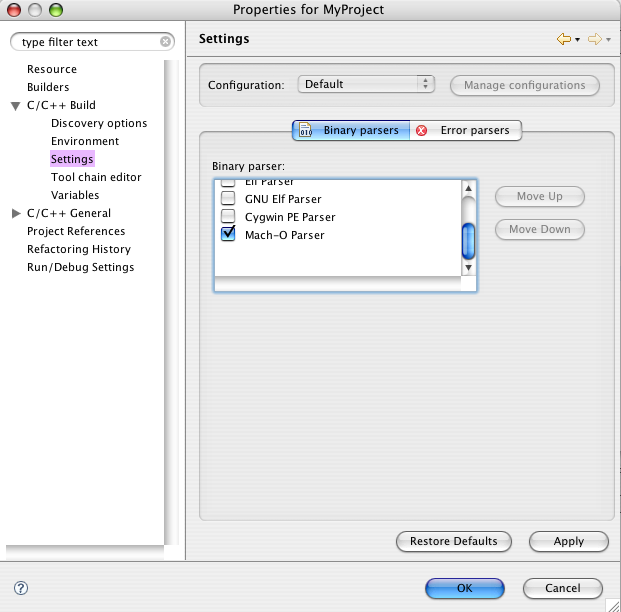
Disclose the "C/C++ Build" options, and select "Settings".
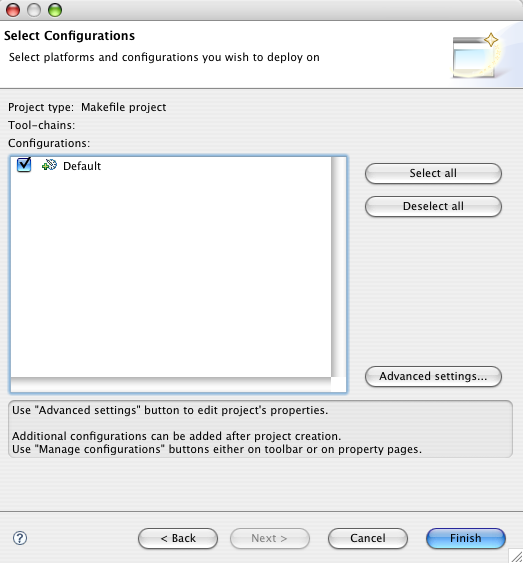
In the Right Side pane select the binary format for your system. Click on the OK Button. Your project is now ready.
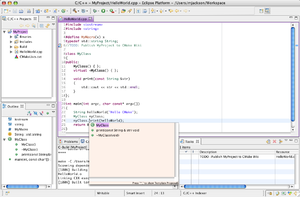
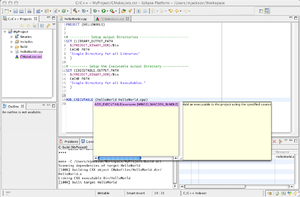
| Our Finished Project showing off some of the C++ semantic highlighting capabilities |
Eclipse showing the CMakeEditor Plugin |
|---|---|
Creating an External Tool to run cmake (Optional)
In the course of normal development it is common to edit your CMakeLists.txt files. The makefile should pick up this difference and rerun cmake again. Most of the time this is perfectly sufficient and works just fine. Othertimes however this is NOT sufficient so having a convenient way to run CMake from within Eclipse is handy.
Times when this step is needed:
- You do major edits to the CMakeLists.txt files and you want to be sure that cmake is picking everything up.
- You would like to start from a clean build state with nothing in the build directory
- You are developing your CMakeLists.txt file and you just want to see the outcome of running cmake on your project but do NOT need to actually build your project. For example you are configuring a file and just want to see the newly created/configured file
Creating an External Tool
To do this select the "Run->External Tools->Show External Tools Dialog..." menu.
Create a new "Program" and call it Cmake.
In the "Location" text field, type the absolute path to cmake (/usr/local/bin/cmake).
In the "Working Directory" test field insert the following: "${project_loc}/Build" and in the Arguments section insert the following: "../".
In the "Refresh" tab select The project containing the selected resources.
In the "Common" tab check the "External Tools" selection.
This will put a shortcut in the "Run" menu for you.
Click the Apply Button and then run.
CMake will now run on your project directory.
Parsing Errors more efficiently
The CDT Error Parser cannot handle error messages that span more than one line, which is the default gcc behavior. In order to force gcc to generate single line error messages with no line wrapping, add to your CMakeLists.txt:
IF(CMAKE_COMPILER_IS_GNUCC)
SET(CMAKE_C_FLAGS "${CMAKE_C_FLAGS} -fmessage-length=0")
ENDIF(CMAKE_COMPILER_IS_GNUCC)
IF(CMAKE_COMPILER_IS_GNUCXX)
SET(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -fmessage-length=0")
ENDIF(CMAKE_COMPILER_IS_GNUCXX)
Automatic Discovery of Include directories (Optional, but handy)
Eclipse relies on default include paths such as /usr/include to find and index header files. One can manually enter more include paths from the "Project Properties" dialog but there is a much easier way for Eclipse to pick up on any 'non-default' include paths needed by your project.
Eclipse has a mechanism in place to 'Discover' these locations. The mechanism works by parsing the compiler invocation looking for "-I" arguments then adds these directories to the list of include paths to index. In order for this discovery process to work you need to build your project at least once with the CMAKE_VERBOSE_MAKEFILE to true either by setting the variable in your CMakeLists.txt file
SET(CMAKE_VERBOSE_MAKEFILE ON)
OR
by setting the "make" command to the following:
make -C ${project_loc}/Build VERBOSE=1
Multiple Make Jobs for Multi-Core Hardware
If you have a multi-core hardware system (Intel Core Duo or the like) you can use the following to invoke more than one compile job:
make -C ${project_loc}/Build -j2
Where '2' is the number of jobs to have make run.
True Out of Source Builds
You can still do out of source builds if you want. The make command would be the following if you have created your build directory at the same level as your project directory and called it "MyProjectBuild"
make -C ${project_loc}/../MyProjectBuild
While this will work, what you will be missing is the list of binaries in your project view which makes setup of Debugging and Running your executable easier. All this can still be setup through custom run and debug commands in eclipse. I will leave that as an exercise to the reader.