Apply a Filter to a Specified Region of an Image¶
Synopsis¶
Computes the derivative of an image in a particular direction.
Results¶
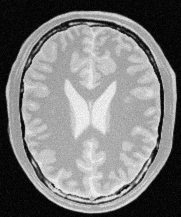
Input image¶
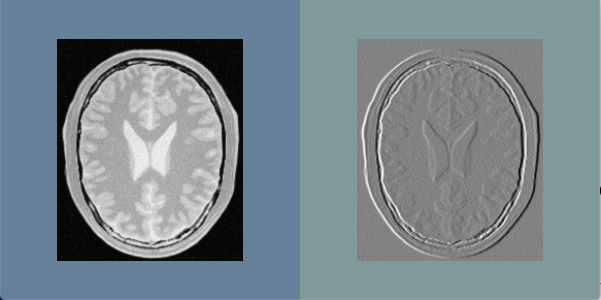
Output in QuickView¶
Code¶
C++¶
#include "itkImage.h"
#include "itkImageFileReader.h"
#include "itkDerivativeImageFilter.h"
#ifdef ENABLE_QUICKVIEW
# include "QuickView.h"
#endif
int
main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
// Verify command line arguments
if (argc < 2)
{
std::cerr << "Usage: " << std::endl;
std::cerr << argv[0] << " inputImageFile" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// Parse command line arguments
std::string inputFilename = argv[1];
// Setup types
using FloatImageType = itk::Image<float, 2>;
using UnsignedCharImageType = itk::Image<unsigned char, 2>;
using readerType = itk::ImageFileReader<UnsignedCharImageType>;
using filterType = itk::DerivativeImageFilter<UnsignedCharImageType, FloatImageType>;
// Create and setup a reader
readerType::Pointer reader = readerType::New();
reader->SetFileName(inputFilename.c_str());
// Create and setup a derivative filter
filterType::Pointer derivativeFilter = filterType::New();
derivativeFilter->SetInput(reader->GetOutput());
derivativeFilter->SetDirection(0); // "x" axis
#ifdef ENABLE_QUICKVIEW
QuickView viewer;
viewer.AddImage<UnsignedCharImageType>(reader->GetOutput());
viewer.AddImage<FloatImageType>(derivativeFilter->GetOutput());
viewer.Visualize();
#endif
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Classes demonstrated¶
-
template<typename
TInputImage, typenameTOutputImage>
classDerivativeImageFilter: public itk::ImageToImageFilter<TInputImage, TOutputImage> Computes the directional derivative of an image. The directional derivative at each pixel location is computed by convolution with a derivative operator of user-specified order.
SetOrder specifies the order of the derivative.
SetDirection specifies the direction of the derivative with respect to the coordinate axes of the image.
- See
Image
- See
Neighborhood
- See
NeighborhoodOperator
- See
NeighborhoodIterator
- ITK Sphinx Examples:

