Normalize Image¶
Synopsis¶
Normalize an image.
Results¶
Input Image¶

Input And Output Image With Data¶
Code¶
C++¶
#include "itkImage.h"
#include "itkImageFileReader.h"
#include "itkNormalizeImageFilter.h"
#include "itkStatisticsImageFilter.h"
#ifdef ENABLE_QUICKVIEW
# include "QuickView.h"
#endif
#include <iomanip>
int
main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
if (argc < 2)
{
std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " filename" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
using FloatImageType = itk::Image<double, 2>;
using ReaderType = itk::ImageFileReader<FloatImageType>;
ReaderType::Pointer reader = ReaderType::New();
reader->SetFileName(argv[1]);
using NormalizeFilterType = itk::NormalizeImageFilter<FloatImageType, FloatImageType>;
NormalizeFilterType::Pointer normalizeFilter = NormalizeFilterType::New();
normalizeFilter->SetInput(reader->GetOutput());
using StatisticsFilterType = itk::StatisticsImageFilter<FloatImageType>;
StatisticsFilterType::Pointer statistics1 = StatisticsFilterType::New();
statistics1->SetInput(reader->GetOutput());
StatisticsFilterType::Pointer statistics2 = StatisticsFilterType::New();
statistics2->SetInput(normalizeFilter->GetOutput());
#ifdef ENABLE_QUICKVIEW
QuickView viewer;
std::stringstream desc1;
statistics1->Update();
desc1 << itksys::SystemTools::GetFilenameName(argv[1]) << "\nMean: " << statistics1->GetMean()
<< " Variance: " << statistics1->GetVariance();
viewer.AddImage(reader->GetOutput(), true, desc1.str());
std::stringstream desc2;
statistics2->Update();
desc2 << "Normalize"
<< "\nMean: " << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << statistics2->GetMean()
<< " Variance: " << statistics2->GetVariance();
viewer.AddImage(normalizeFilter->GetOutput(), true, desc2.str());
viewer.Visualize();
#endif
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Classes demonstrated¶
-
template<typename
TInputImage, typenameTOutputImage>
classNormalizeImageFilter: public itk::ImageToImageFilter<TInputImage, TOutputImage> Normalize an image by setting its mean to zero and variance to one.
NormalizeImageFilter shifts and scales an image so that the pixels in the image have a zero mean and unit variance. This filter uses StatisticsImageFilter to compute the mean and variance of the input and then applies ShiftScaleImageFilter to shift and scale the pixels.
NB: since this filter normalizes the data such that the mean is at 0, and
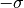 to
to 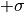 is mapped to -1.0 to 1.0, output image integral types will produce an image that DOES NOT HAVE a unit variance due to 68% of the intensity values being mapped to the real number range of -1.0 to 1.0 and then cast to the output integral value.
is mapped to -1.0 to 1.0, output image integral types will produce an image that DOES NOT HAVE a unit variance due to 68% of the intensity values being mapped to the real number range of -1.0 to 1.0 and then cast to the output integral value.- See
NormalizeToConstantImageFilter
- ITK Sphinx Examples:

