 |
ITK
5.2.0
Insight Toolkit
|
 |
ITK
5.2.0
Insight Toolkit
|
#include <itkNormalizeImageFilter.h>
 Inheritance diagram for itk::NormalizeImageFilter< TInputImage, TOutputImage >:
Inheritance diagram for itk::NormalizeImageFilter< TInputImage, TOutputImage >: Collaboration diagram for itk::NormalizeImageFilter< TInputImage, TOutputImage >:
Collaboration diagram for itk::NormalizeImageFilter< TInputImage, TOutputImage >:Static Public Member Functions | |
| static Pointer | New () |
 Static Public Member Functions inherited from itk::ImageToImageFilter< TInputImage, TOutputImage > Static Public Member Functions inherited from itk::ImageToImageFilter< TInputImage, TOutputImage > | |
| static void | SetGlobalDefaultDirectionTolerance (double) |
| static double | GetGlobalDefaultDirectionTolerance () |
| static void | SetGlobalDefaultCoordinateTolerance (double) |
| static double | GetGlobalDefaultCoordinateTolerance () |
 Static Public Member Functions inherited from itk::Object Static Public Member Functions inherited from itk::Object | |
| static bool | GetGlobalWarningDisplay () |
| static void | GlobalWarningDisplayOff () |
| static void | GlobalWarningDisplayOn () |
| static Pointer | New () |
| static void | SetGlobalWarningDisplay (bool val) |
 Static Public Member Functions inherited from itk::LightObject Static Public Member Functions inherited from itk::LightObject | |
| static void | BreakOnError () |
| static Pointer | New () |
Private Attributes | |
| ShiftScaleImageFilter< TInputImage, TOutputImage >::Pointer | m_ShiftScaleFilter |
| StatisticsImageFilter< TInputImage >::Pointer | m_StatisticsFilter |
Normalize an image by setting its mean to zero and variance to one.
NormalizeImageFilter shifts and scales an image so that the pixels in the image have a zero mean and unit variance. This filter uses StatisticsImageFilter to compute the mean and variance of the input and then applies ShiftScaleImageFilter to shift and scale the pixels.
NB: since this filter normalizes the data such that the mean is at 0, and 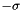 to
to 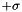 is mapped to -1.0 to 1.0, output image integral types will produce an image that DOES NOT HAVE a unit variance due to 68% of the intensity values being mapped to the real number range of -1.0 to 1.0 and then cast to the output integral value.
is mapped to -1.0 to 1.0, output image integral types will produce an image that DOES NOT HAVE a unit variance due to 68% of the intensity values being mapped to the real number range of -1.0 to 1.0 and then cast to the output integral value.
Definition at line 54 of file itkNormalizeImageFilter.h.
| using itk::NormalizeImageFilter< TInputImage, TOutputImage >::ConstPointer = SmartPointer<const Self> |
Definition at line 63 of file itkNormalizeImageFilter.h.
| using itk::NormalizeImageFilter< TInputImage, TOutputImage >::InputImagePointer = typename TInputImage::Pointer |
Image related type alias.
Definition at line 72 of file itkNormalizeImageFilter.h.
| using itk::NormalizeImageFilter< TInputImage, TOutputImage >::OutputImagePointer = typename TOutputImage::Pointer |
Definition at line 73 of file itkNormalizeImageFilter.h.
| using itk::NormalizeImageFilter< TInputImage, TOutputImage >::Pointer = SmartPointer<Self> |
Definition at line 62 of file itkNormalizeImageFilter.h.
| using itk::NormalizeImageFilter< TInputImage, TOutputImage >::Self = NormalizeImageFilter |
Standard Self type alias
Definition at line 60 of file itkNormalizeImageFilter.h.
| using itk::NormalizeImageFilter< TInputImage, TOutputImage >::Superclass = ImageToImageFilter<TInputImage, TOutputImage> |
Definition at line 61 of file itkNormalizeImageFilter.h.
|
protected |
|
virtual |
Create an object from an instance, potentially deferring to a factory. This method allows you to create an instance of an object that is exactly the same type as the referring object. This is useful in cases where an object has been cast back to a base class.
Reimplemented from itk::Object.
|
overrideprotectedvirtual |
GenerateData.
Reimplemented from itk::ImageSource< TOutputImage >.
|
overrideprotectedvirtual |
What is the input requested region that is required to produce the output requested region? The base assumption for image processing filters is that the input requested region can be set to match the output requested region. If a filter requires more input (for instance a filter that uses neighborhoods needs more input than output to avoid introducing artificial boundary conditions) or less input (for instance a magnify filter) will have to override this method. In doing so, it should call its superclass' implementation as its first step. Note that imaging filters operate differently than the classes to this point in the class hierarchy. Up till now, the base assumption has been that the largest possible region will be requested of the input.
This implementation of GenerateInputRequestedRegion() only processes the inputs that are a subclass of the ImageBase<InputImageDimension>. If an input is another type of DataObject (including an Image of a different dimension), they are skipped by this method. The subclasses of ImageToImageFilter are responsible for providing an implementation of GenerateInputRequestedRegion() when there are multiple inputs of different types.
Reimplemented from itk::ImageToImageFilter< TInputImage, TOutputImage >.
|
virtual |
Runtime information support.
Reimplemented from itk::ImageToImageFilter< TInputImage, TOutputImage >.
|
overridevirtual |
NormalizeImageFilter must call modified on its internal filters
Reimplemented from itk::Object.
|
static |
Method for creation through the object factory.
|
private |
Definition at line 93 of file itkNormalizeImageFilter.h.
|
private |
Definition at line 91 of file itkNormalizeImageFilter.h.
 1.8.16
1.8.16