Smooth Image While Preserving Edges¶
Synopsis¶
Smooth an image while preserving edges.
Results¶

Input image.¶
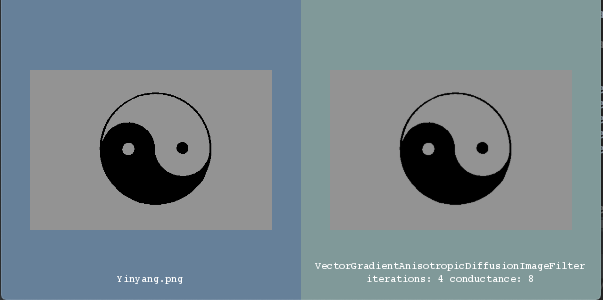
Output In VTK Window¶
Code¶
C++¶
#include "itkImage.h"
#include "itkCastImageFilter.h"
#include "itkImageFileReader.h"
#include "itkVectorGradientAnisotropicDiffusionImageFilter.h"
#include "itkVectorToRGBImageAdaptor.h"
#include "itkRGBToVectorImageAdaptor.h"
#include "itkCastImageFilter.h"
#include "itksys/SystemTools.hxx"
#include <sstream>
#ifdef ENABLE_QUICKVIEW
# include "QuickView.h"
#endif
int
main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
// Verify arguments
if (argc < 2)
{
std::cerr << "Usage: " << std::endl;
std::cerr << argv[0];
std::cerr << " InputFileName";
std::cerr << " [NumberOfIterations] ";
std::cerr << " [Conductance]" << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
// 0) Parse arguments
std::string inputFileName = argv[1];
using FloatImageType = itk::Image<itk::Vector<float, 3>, 2>;
using RGBImageType = itk::Image<itk::RGBPixel<float>, 2>;
// 1) Read the RGB image
using ReaderType = itk::ImageFileReader<RGBImageType>;
ReaderType::Pointer reader = ReaderType::New();
reader->SetFileName(inputFileName);
// 2) Cast to Vector image for processing
using AdaptorInputType = itk::RGBToVectorImageAdaptor<RGBImageType>;
AdaptorInputType::Pointer adaptInput = AdaptorInputType::New();
adaptInput->SetImage(reader->GetOutput());
using CastInputType = itk::CastImageFilter<AdaptorInputType, FloatImageType>;
CastInputType::Pointer castInput = CastInputType::New();
castInput->SetInput(adaptInput);
// 3) Smooth the image
using VectorGradientAnisotropicDiffusionImageFilterType =
itk::VectorGradientAnisotropicDiffusionImageFilter<FloatImageType, FloatImageType>;
VectorGradientAnisotropicDiffusionImageFilterType::Pointer filter =
VectorGradientAnisotropicDiffusionImageFilterType::New();
filter->SetInput(castInput->GetOutput());
filter->SetTimeStep(0.125);
if (argc > 2)
{
filter->SetNumberOfIterations(atoi(argv[2]));
}
if (argc > 3)
{
filter->SetConductanceParameter(atof(argv[3]));
}
// 4) Cast the Vector image to an RGB image for display
using AdaptorOutputType = itk::VectorToRGBImageAdaptor<FloatImageType>;
AdaptorOutputType::Pointer adaptOutput = AdaptorOutputType::New();
adaptOutput->SetImage(filter->GetOutput());
using CastOutputType = itk::CastImageFilter<AdaptorOutputType, RGBImageType>;
CastOutputType::Pointer castOutput = CastOutputType::New();
castOutput->SetInput(adaptOutput);
// 5) Display the input and smoothed images
#ifdef ENABLE_QUICKVIEW
QuickView viewer;
viewer.AddRGBImage(reader->GetOutput(), true, itksys::SystemTools::GetFilenameName(inputFileName));
std::stringstream desc;
desc << "VectorGradientAnisotropicDiffusionImageFilter\niterations: " << filter->GetNumberOfIterations()
<< " conductance: " << filter->GetConductanceParameter();
viewer.AddRGBImage(castOutput->GetOutput(), true, desc.str());
viewer.Visualize();
#endif
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
Classes demonstrated¶
-
template<typename
TInputImage, typenameTOutputImage>
classVectorGradientAnisotropicDiffusionImageFilter: public itk::AnisotropicDiffusionImageFilter<TInputImage, TOutputImage> This filter performs anisotropic diffusion on a vector itk::Image using the anisotropic diffusion function implemented implemented in itkVectorGradientNDAnisotropicDiffusionFunction. For detailed information on anisotropic diffusion see itkAnisotropicDiffusionFunction, itkVectorGradientNDAnisotropicDiffusionFunction, and itkGradientAnisotropicDiffusionFunction.
The maximum allowable time step for this filter is 1/2^N, where N is the dimensionality of the image. For 2D images any value below 0.250 is stable, and for 3D images, any value below 0.125 is stable.
- Inputs and Outputs
The input to this filter must be an itk::Image with pixel type which is either an itk::Vector, or a subclass of an itk::Vector. Additionally, the component type of the vector should be a numerical type (float or double, or a user defined type which correctly defines arithmetic operations with floating point accuracy). The output image type also has these requirements.
- Parameters
Please read all the documentation found in AnisotropicDiffusionImageFilter and AnisotropicDiffusionFunction. Also see VectorGradientNDAnisotropicDiffusionFunction.
- ITK Sphinx Examples:

